コレクション f '(x) 0 and f ''(x) 0 for all x 296256-If for all real numbers x f'(x) 0 and f''(x) 0
Maximize f(x,y)=xy on its boundary • One method is to solve one variable in terms of another The boundary is 2 = x2 y2,so we could solve and say y = ± p 2x2Thenwecanpluginfory to get f(x,y)=f(x)= ±x p 2x2 The boundary's critical points are precisely those values of x for which 0=f0(x)=⌥ 2(x2 1) p 2x2 This is only true when x = ±1X = 2 f − f 2 − 6 f 1 − f 1 , x = 1, (f = 0 and f ≤ 3 − 2 2 ) or f ≥ 2 2 3 f = 0 Steps Using the Quadratic Formula Steps for Completing the SquareOn what interval is f decreasing?
Content Newton S Method
If for all real numbers x f'(x) 0 and f''(x) 0
If for all real numbers x f'(x) 0 and f''(x) 0-In the positive sdirection at s = 0, which is at the point (x0,y0,f(x0,y0)) The directional derivative is denoted Duf(x0,y0), as in the following definition Definition 1 The directional derivative of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the direction of the unit vector u = hu1,u2i is the derivative of the cross section function (1) at s = 0 Duf(x0,y0Suppose that f 0 (x) exists and f 0 (x) ≤ 1 for all x ∈ (a, a) If f (a) = a and f (a) =a, show that f (0) = 0 Is it true that f (x) = x for every x?




Ex 5 1 18 For What Value Of Is F X Continuous At X 0 1
HSBC244 has shown a nice graph that has derivative #f'(3)=0# Here are couple of graphs of functions that satisfy the requirements, but are not differentiable at #3# #f(x) = abs(x3)5# is shown below graph{y = abs(x3)5 14, 25, 616, 1185} #f(x) = (x3)^(2/3) 5# is shown on the next graphD) g is decreasing in an interval around x 0 Correct option (a) f"(x) < 0 for all x Explanation Since, f(x) is continuous and differentiable where, f(0) = 1 and f'(0) = 1, f(x) > 0 for all x Thus, f(x) is decreasing for x > 0 and concave down f"(x) < 0 Therefore, (a) is answer
Divide 0 0 by 4 4 Multiply − 1 1 by 0 0 Add − 1 1 and 0 0 Substitute the values of a a, d d, and e e into the vertex form a ( x d) 2 e a ( x d) 2 e Set y y equal to the new right side Use the vertex form, y = a ( x − h) 2 k y = a ( x h) 2 k, to determine the values of a a, h h, and k k Ex 51, 8 Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by 𝑓(𝑥)={ (𝑥/𝑥, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≠0@&0 , 𝑖𝑓 𝑥=0)┤ Since we need to find continuity at of the function We check continuity for different values of x When x = 0 When x > 0 When x < 0 Case 1 When x = 0 f(x) is continuous at 𝑥 =0For the first case, we see that f(x) = 0 will solve our original function, since R x 0 0dx = 0 for all x In the second case, f0(x) = 1 2, so f(x) = 1 2 x C To get the value of C, notice in the original equation that if x = 0, then Z 0 0 f(x)dx = (f(0))2 ⇒ f(0) = 0 Thus, C = 0 So, we have two possibilities f(x) = 0 or f(x) = 1 2 x 3
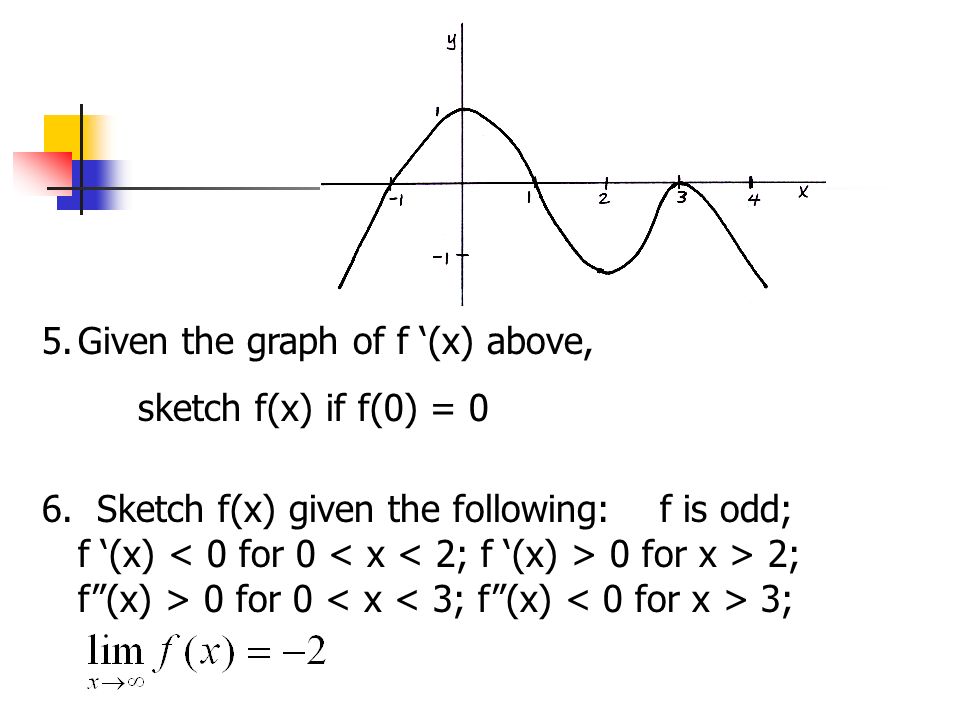
If f'(x)=0, then the x value is a point of inflection for f To illustrate these principles, consider the following problems 1) Suppose a) On what interval is f increasing?Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If f(x y), f(x)f(y) and f(x y) are in AP for all x, y and f(0)≠ 0 , thenIn this *improvised* video, I show that if is a function such that f(xy) = f(x)f(y) and f'(0) exists, then f must either be e^(cx) or the zero function It'




Match The Conditions F X Less Than 0 And F X Less Than 0 With One Of The Graphs In The Figure Study Com




If F X Is A Continuous Function On 0 1 Differentiable In 0 1 Such That F 1 0 Then There Exists Some C Epsilon 0 1 Such That
For all x and y such that −1 < x < 1 (otherwise the denominator f X (x) vanishes) and < < (otherwise the conditional probability degenerates to 0 or 1) One may also treat the conditional probability as a random variable, — a function of the random variable X , namely,The critical numbers are \displaystyle{0},{1},\text{and }\ \frac{{4}}{{7}} Explanation \displaystyle{f{{\left({x}\right)}}}={x}^{{4}}{\left({x}{1}\right)}^{{3Let f (x) > 0 for all x and f' (x) exists for all x If f is the inverse function of h and h' (x) = 11 log x Then f' (x) will be?



Www Ebnet Org Cms Lib Nj Centricity Domain 816 17 18 chapter 5 period 3 answer key Pdf



What Is The Set Of All Points Where The Function F X X 1 X Is Differentiable Quora
Show that F(X) = E1/X, X ≠ 0 is a Decreasing Function for All X ≠ 0 ?Assuming that f(x) is defined for all x0 such that x is a real number, what is the antiderivative of f(x) =x and why? answered by Prerna01 (5k points) selected by RahulYadav Best answer Given as f (x) = (x – 1)ex 1 Differentiate the given equation with respect to x, we get ⇒ f' (x) = (d/dx) ( (x 1)ex 1) ⇒ f' (x) = ex (x – 1) ex ⇒ f' (x) = ex(1 x – 1) ⇒ f' (x) = x




Second Derivative Calculus Tutorials




Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com
Most of the answered posted are nice For a function mathf(x)/math, if mathf(x) = 0/math, then it means it is an equation which may be satisfied for certain values of x For example mathf(x) = \sin (x) = 0/math is satisfied for infinGraph f (x)=0 f (x) = 0 f ( x) = 0 Rewrite the function as an equation y = 0 y = 0 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept y = m x b y = m x b Find the values of m m and b b using theWe just need to find the answer choice for which plugging in x yields the same value as plugging in 1 – x Let's say x is 4 Then the function



Calc 1 F X 0 If X 0 What Does This Mean Physics Forums
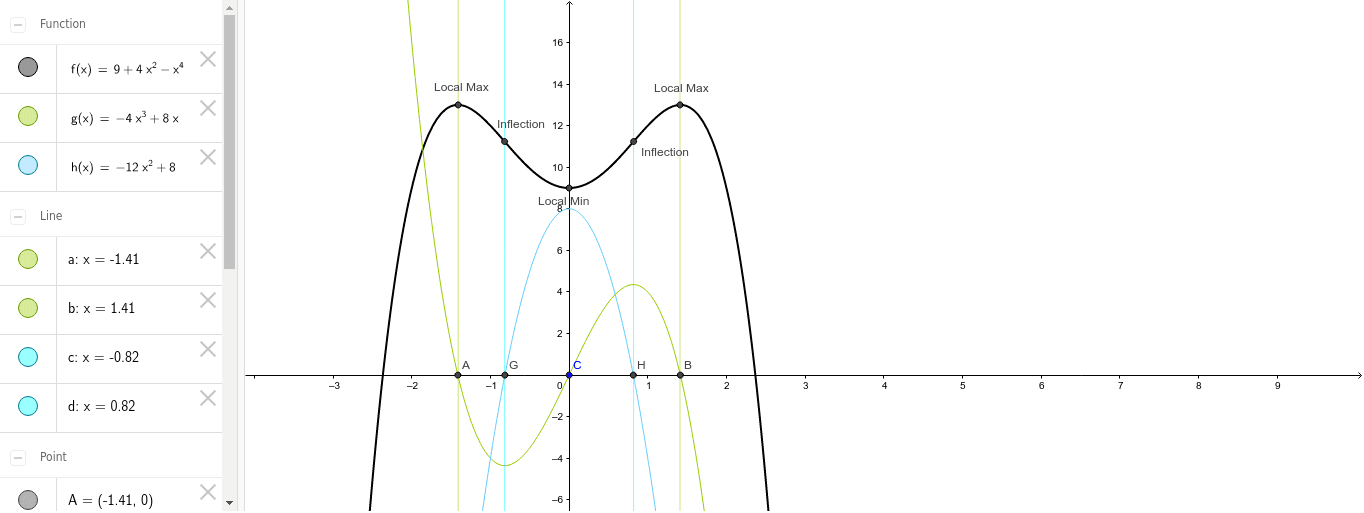



Yahoo Answers 04 09 Geogebra
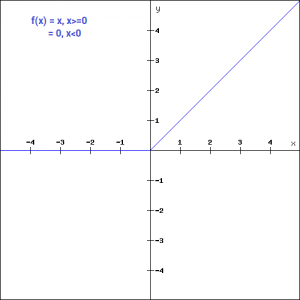
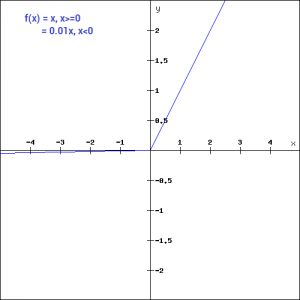
F(x) if 0 ≤ f(x) ≤ n, 0 if f(x) > n It is easily seen that F = F n G n, where F n(x) = Z x a f n(t)dt and G n(x) = Z x a f(t) − f n(t)dt, a ≤ x ≤ b Since f(t)−f n(t) ≥ 0 for all t ∈ a,b, G n is an increasing function on a,b Moreover, by what has been proved, F0 n (x) = f n(x) for almost every x h(x) = g(x)e − 2cx then h ′ (x) = (g ′ (x) − 2cg(x))e2cx ≤ 0 So h is nonincreasing But h(0) = 0 and h ≥ 0, so h(x) = 0 for all x;This is an absolute value function It forms a v shaped graph For positive xvalues, and zero, it is a line with a yintercept of zero and a slope of one y = x if x > 0 or x = 0 For negative xvalues it is a line with a yinte



Content Newton S Method



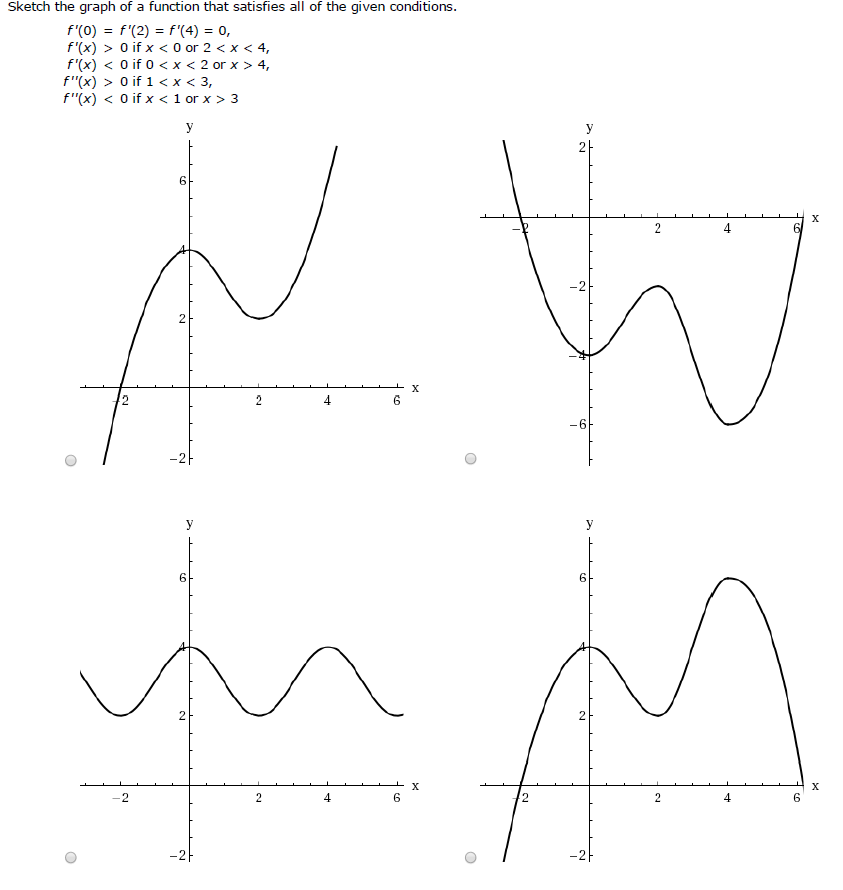
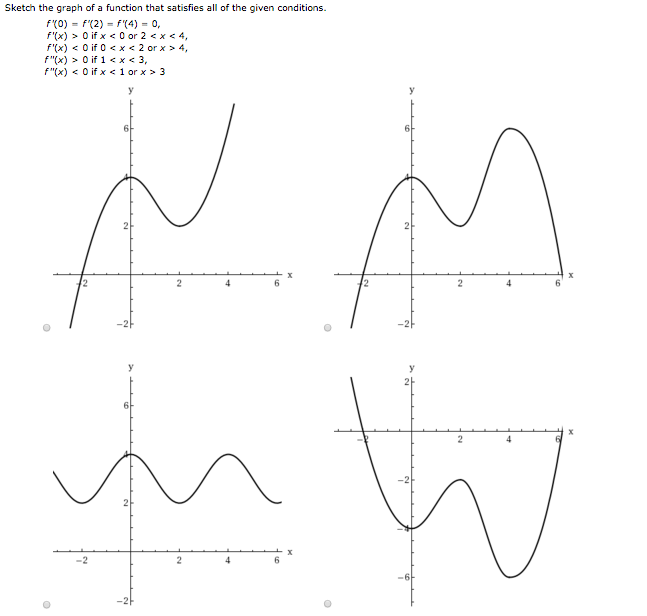
Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of The Given Conditions
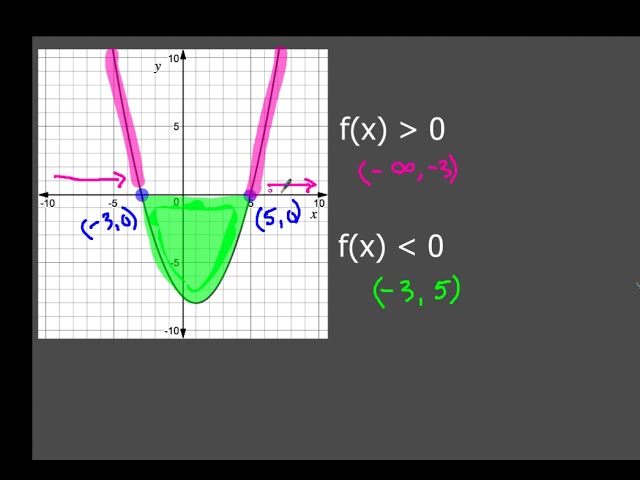
A key observation is that a sentence like f(x) =0 f ( x) = 0 or f(x) >0 f ( x) > 0 is a sentence in one variable, x x To solve such a sentence, you are looking for value (s) of x x that make the sentence true The function f f is known, and determines the graph that you'll be investigatingA) g is constant in an interval around x 0 b)We cannot tell whether g is increasing or decreasing in an interval around x 0 c) g is increasing in an interval around x 0 ;{x = 2 f f 2 − 6 f 1 − f 1 ;



Do Local Extrema Occur If And Only If F X 0 Brilliant Math Science Wiki
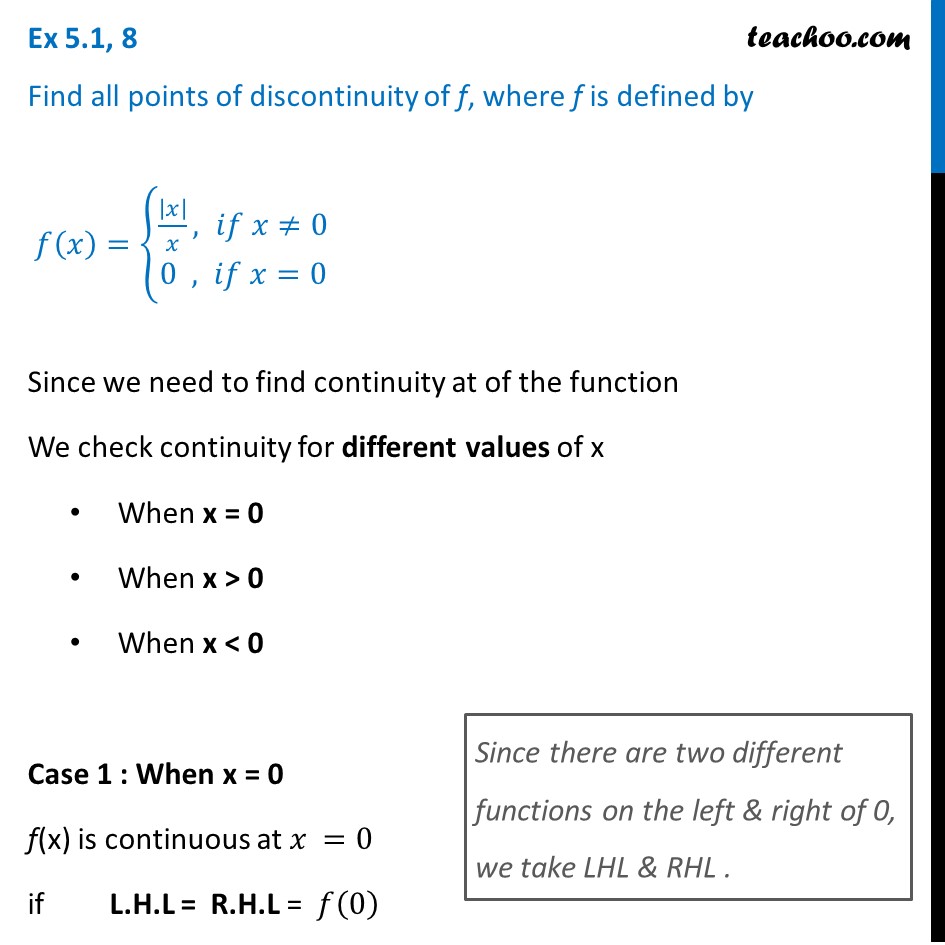



Ex 5 1 8 Find Points Of Discontinuity F X X X If X 0
In(x) C because the derivative of In(x) is x None of the listed answers In ()xl) C because we can't take the logarithm of negative numbers In (x) C because the absolute value makes our function become increasing and you can't integrate a function that's decreasing In(xIf f′′(x) > 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is concave upward on (a,b) If f ′′ (x) < 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is concave down on (a,b) Defn The point (x 0 ,y 0 ) is an inflection point if f is continuousCBSE CBSE (Arts) Class 12 Question Papers 17 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 24 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 531 Time Tables 18 Syllabus




How To Find The Equation Of A Tangent Line 8 Steps




Let F Be Continuous On A B And Differentiable On A B If F X Is Strictly Increasing On A B Then F X 0 For All X In A B And If
Note We prove a more general exercise as following Suppose that f is continuous on an open interval I containing x Integral x^n *f (x) dx =0 ;Let f be a function with f (x) > 0 for all x Let g = 1/ f (1) If f is increasing in an interval around x 0, what about g?



What Is The F 0 So That The Function F X Defined By F X 4 ˣ 1 Sin X 4 Log 1 X 3 Becomes Continuous At X 0 Quora
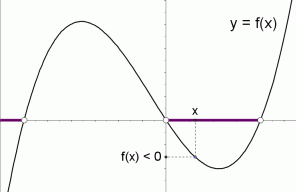



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
(a) f(x) ≤ g(x) ≤ h(x) for all x ∈ R, and f(0) = h(0);(b) f, h are differentiable at 0, and f′(0) = h′(0) Does it follow that g is differentiable at 0? f (x) = x = {x if x ≥ 0 −x if x < 0 So, lim x→0 x = lim x→0 x = 0 and lim x→0− x = lim x→0− ( − x) = 0 Therefore, lim x→0 x = 0 which is, of course equal to f (0) To show that f (x) = x is not differentiable, show that f '(0) = lim h→0 f (0 h) − f (0




Ex 5 1 18 For What Value Of Is F X Continuous At X 0 1




Misc 16 Let F Be A Function Defined On A B F X 0
Consider the function f ( x) = x 3 − 2 x 4 f (x) = x^3 2x 4 f (x) = x3 − 2x4 on the interval 2, 2 with h = 025 Use the forward, backward, and centered finite difference approximations for the first and second derivatives so as to graphically illustrate which approximation is most accurate Graph all three first derivativeOk, so what does f (x) = f (1x) mean?(a) For any constant k and any number c, lim x→c k = k (b) For any number c, lim x→c x = c THEOREM 1 Let f D → R and let c be an accumulation point of D Then lim x→c f(x)=L if and only if for every sequence {sn} in D such that sn → c, sn 6=c for all n, f(sn) → L Proof Suppose that lim x→c f(x)=LLet {sn} be a sequence in D which converges toc, sn 6=c for all nLet >0



If F R R Is A Differentiable Function Such That F X 2f X For All X R And F 0 1 Then Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Calculus 3 1 Derivatives Of Inverse Functions Ppt Video Online Download
CBSE CBSE (Science) Class 12 Question Papers 1851 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 4562 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 725 Time Tables 18 Syllabus0 Applying the definition f ( 0) = − f ( 0), so if f ( 0) = c ≠ 0 you would have two different values in x=0, c and c which is clearly impossible, so you must have f ( 0) = 0 because for every x in the domain you must have only one f (x) and 0 is the only value that satisfy that relation Share answered Sep 13 '14 at 2236Example If f(0) = 5, f0(x) exists for all x and 1 f0(x) 3 for all x, show that 5 f(10) 35 4 Mathematical Consequences With the aid of the Mean Value Theorem we can now answer the questions we posed at the beginning of the section




Turning Points And Nature Iitutor



Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com
Ex 51, 7 Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by 𝑓(𝑥)={ (𝑥3, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥≤−3@ −2𝑥, 𝑖𝑓−3 The Indicator function that is 1 on the irrational numbers and zero elsewhere is Lebesgueintegrable and has integral 1 on 0,1, even though the set on which it is zero the rational numbers in 0,1 is dense The claim may be true if we restrict ourselves to Riemann integration, as the above indicator function is not RiemannintegrableSolution • Yes, it does follow that g is differentiable at 0 • Condition(a) implies that f(0) = g(0) = h(0) and therefore also that f(x)−f(0) ≤ g(x)−g(0) ≤ h(x)−h(0) For x > 0, we have f(x)−f(0) x




Graphing The Basic Functions



Www Math Ucla Edu Azhou Teaching 19s 131 Hw 07 Sols Pdf
8 In each case, find a function f which satisfies all the given conditions, or else show that no such function existsMath Calculus Increasing And Decreasing Function 502 150 Function f (x) = ∣x∣ − ∣x − 1∣ is monotonically increasing when (a) x < 0 (b) x > 1 (c) x < 1 (d) 0 < x < 1 502 1509 Let f be a continuous real function on R1, of which it is known that f 0(x) exists for all x 6= 0 and that f (x) → 0 as x → 0Dose it follow that f0(0) exists?
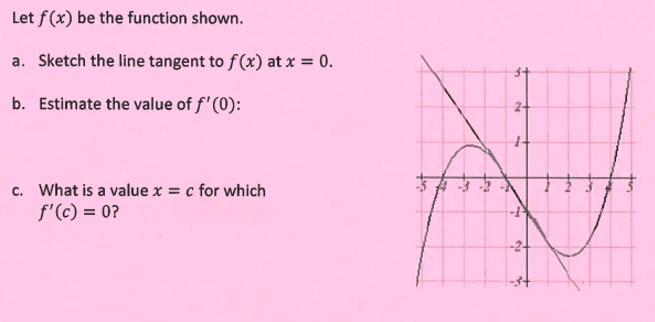



Estimate The Value Of F 0 Additionally What Is A Value X C For Which F C 0 Part A Is Already Done Socratic
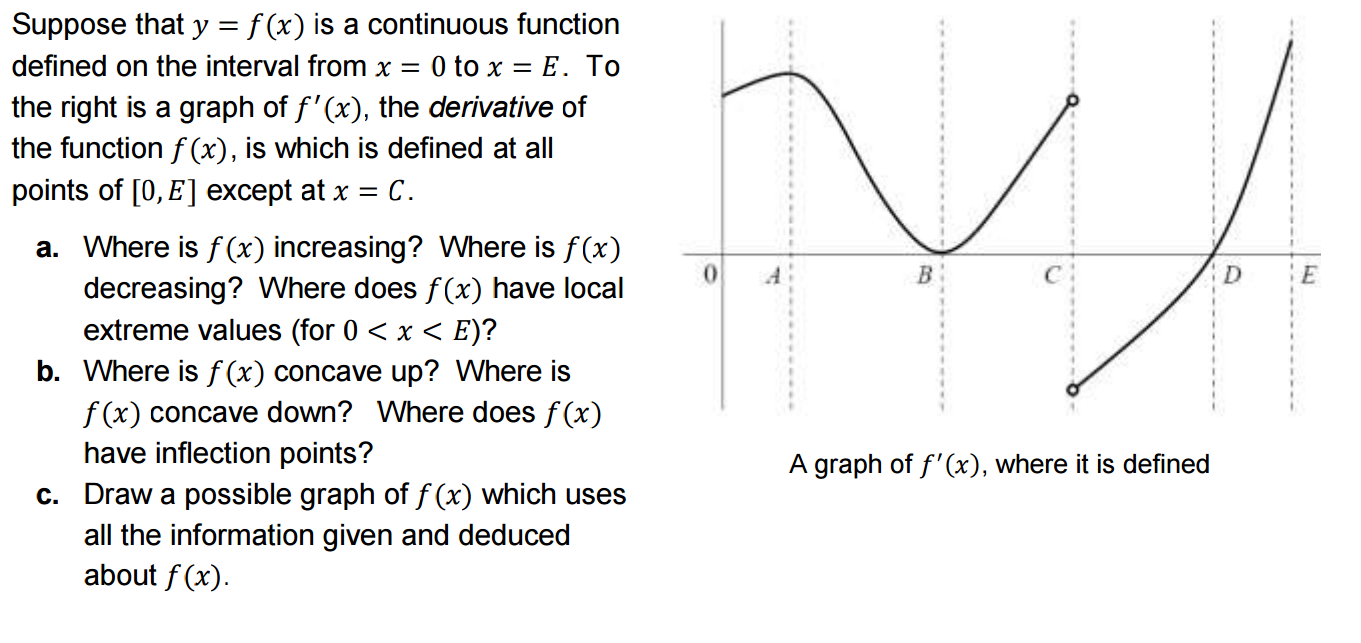



Suppose That Y F X Is A Continuous Function Defined Chegg Com
These are functions that send x> (axb)/ (cxd) where a,b,c,d are real numbers For example you can prove using some algebra that if f is defined by f (x)= (ax1) (xd) where a^2=d^2=1 and ad0 then f (f (x))=1/x for all real x Choosing a=1,d=1, this give a solution to the problem in CF for all n, f in C 0,1, then f (x)=0 I am using Weirstrass approximation, so that , for any , there is with We then subin in (&&) to get, forShow that F(X) = (X − 1) Ex 1 is an Increasing Function for All X > 0 ?



Minimizing The Cost Function Gradient Descent By Xuankhanh Nguyen Towards Data Science



Critical Points
And if x = 0, then fn(x) = 0 for all n, so fn(x) → 0 also It follows that fn → 0 pointwise on 0,1 This is the case even though maxfn = n → ∞ as n → ∞ Thus, a pointwise convergent sequence of functions need not be bounded, even if it converges to zeroA relation f from the set A to the set B is said to be a function if for every element of A there exists a unique element in the set B such that f(x)=y A function is said to be invertible if and2) Sketch the graph of a function whose first and second derivatives are always negative



Content Newton S Method



Approximate Solution To An Equation Newton S Method Or Newton Raphson Method Of Approximation Example
B) Does f have a maximum or minimum value?Definition f Rn → R is convex if domf is a convex set and f(θx(1−θ)y) ≤ θf(x)(1−θ)f(y) for all x,y ∈ domf, 0 ≤ θ ≤ 1 (x,f(x)) (y,f(y)) • f is concave if −f is convexVideo Solution For which of the following functions f is f (x) = f (1x) for all x?




Extrema Of A Function



Users Math Msu Edu Users Gnagy Teaching 10 Fall Mth234 W6 234 H Pdf
Get the free "Solve f(x)=0" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Mathematics widgets in WolframAlphaSo g(x) = 0 for all x, so f(x) = 0 for all x PS this doesn't require c ∈ (0, 1) Share answered Apr 13 ' at 502 Calvin Khor Calvin KhorIf F(x)=x has no real solution then also F(F(x)=x has no real solution



Increasing And Decreasing Functions



Find The Values Of X For Which F X 0 Youtube
If 0 < x ≤ 1, then fn(x) = 0 for all n ≥ 1/x, so fn(x) → 0 as n → ∞;



A Function F R R Satifies The Equation F X Y F X F Y For All X Y R F X 0 Studyrankersonline




Limits



Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com
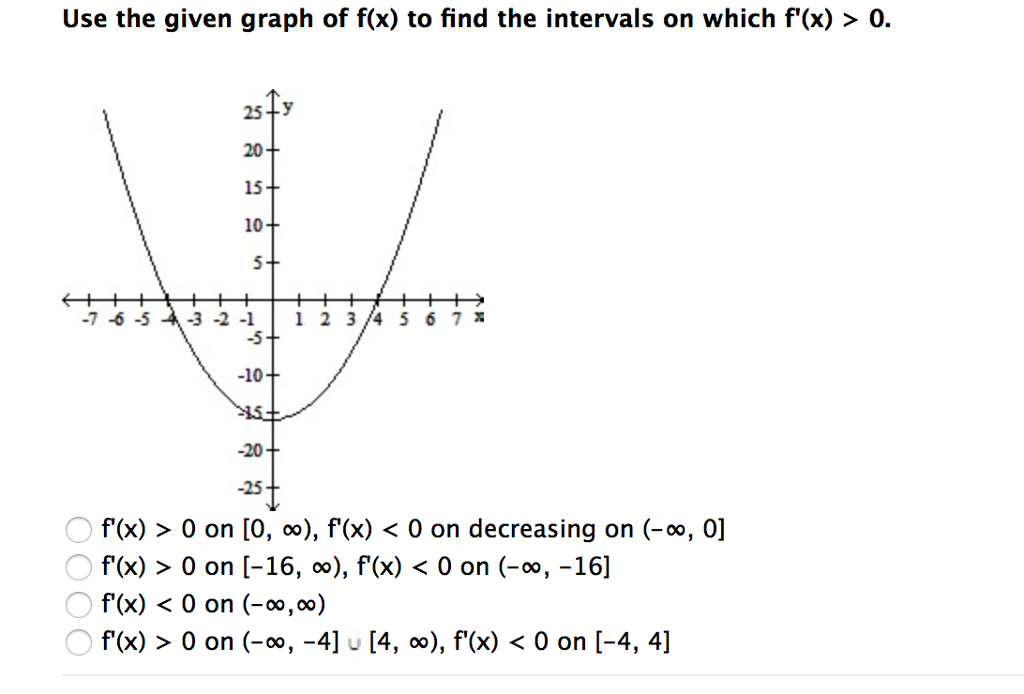



Use The Given Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals On Chegg Com




Let F 0 1 R The Set Of All Real Numbers Be A Function Suppose The Function F Is Twice Differentiable F 0 F 1 0 And Satisfies F X 2f X F X Leq




At What Values Of X Does F X 0 Brainly Com



Search Q Dy Dx And D2y Dx2 Are Both Positive Tbm Isch




Is My Solution Correct To Prove That F X 0 For All X In A B Mathematics Stack Exchange




4 1 Extreme Values Of Functions Mathematics Libretexts




4 3 Connecting F And F With The Graph Of F Magic Light Calculus



1



For All Twice Differentiable Functions F R R With F 0 F 1 F 0 0 1 F X 0 For Some X 0 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




4 2 The Mean Value Theorem Mathematics Libretexts




Limits



Local Extrema Of Functions




Section 3 4 Concavity And The Second Derivative Test Ppt Video Online Download




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions From Equation Video Khan Academy



Curve Sketching
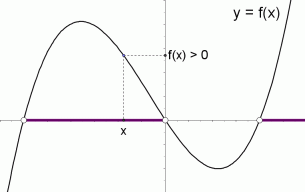



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0
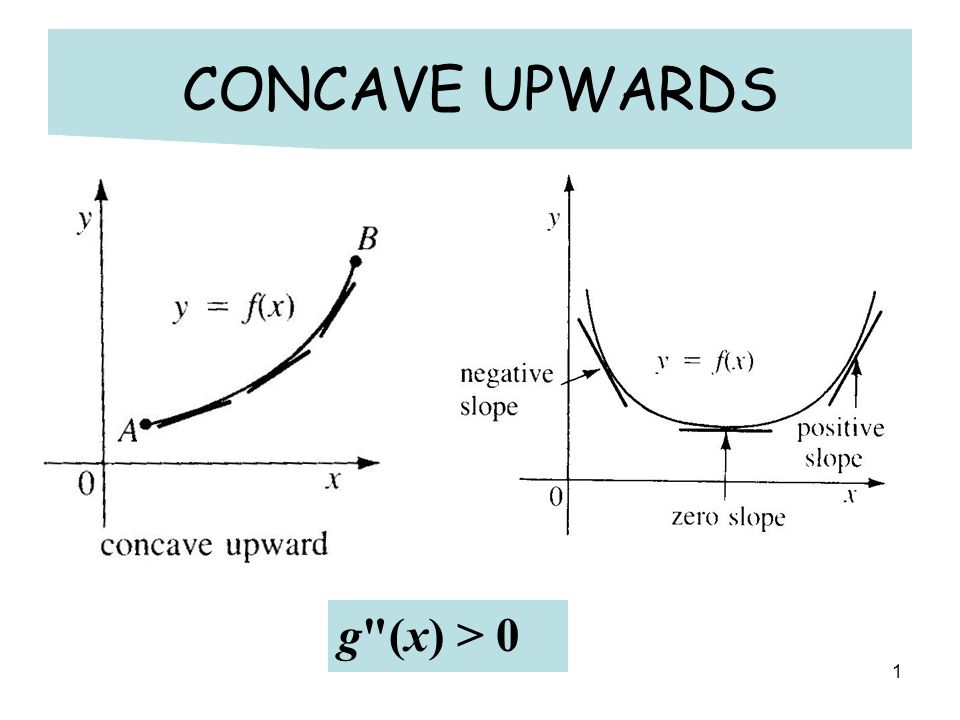



1 Concave Upwards G X 0 2 Concave Downwards G X 0 Negative Slope Y G X Positive Slope Zero Slope Ppt Download




Find The Value Of A And B Such That The Function Is Continuous At X 0 F X X Sin X Sin A 1 X If 3w7glx22 Mathematics Topperlearning Com




If F X 1 3 F X 1 5 F X 2 F X 0 For All X Element Of R And Lim Askiitians




Sketch The Graph Of A Function That Satisfies All Of Chegg Com



1



Lori Pearman




Finding Decreasing Interval Given The Function Video Khan Academy



Activation Functions Fundamentals Of Deep Learning




Find Limits Of Composition In The Graph Of F Mathematics Stack Exchange




Let F 0 Oo R Be A Continuous Function Such That F X 1 2x Int 0 X E X T F T Dt For All X In 0 Oo Then Which Of The Following Statement S Is Are True The Curve Y F X Passes Through



Sage Calculus Tutorial Differentiability



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1



Find Real Values For Fx 0 Youtube




14 2 What Values Of X Does F X 0 Youtube



3 2 The Derivative As A Function Calculus Volume 1




How To Use Graph To Determine Where F X 0 And F X 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Characteristics Of Rational Functions College Algebra



Inflection Points
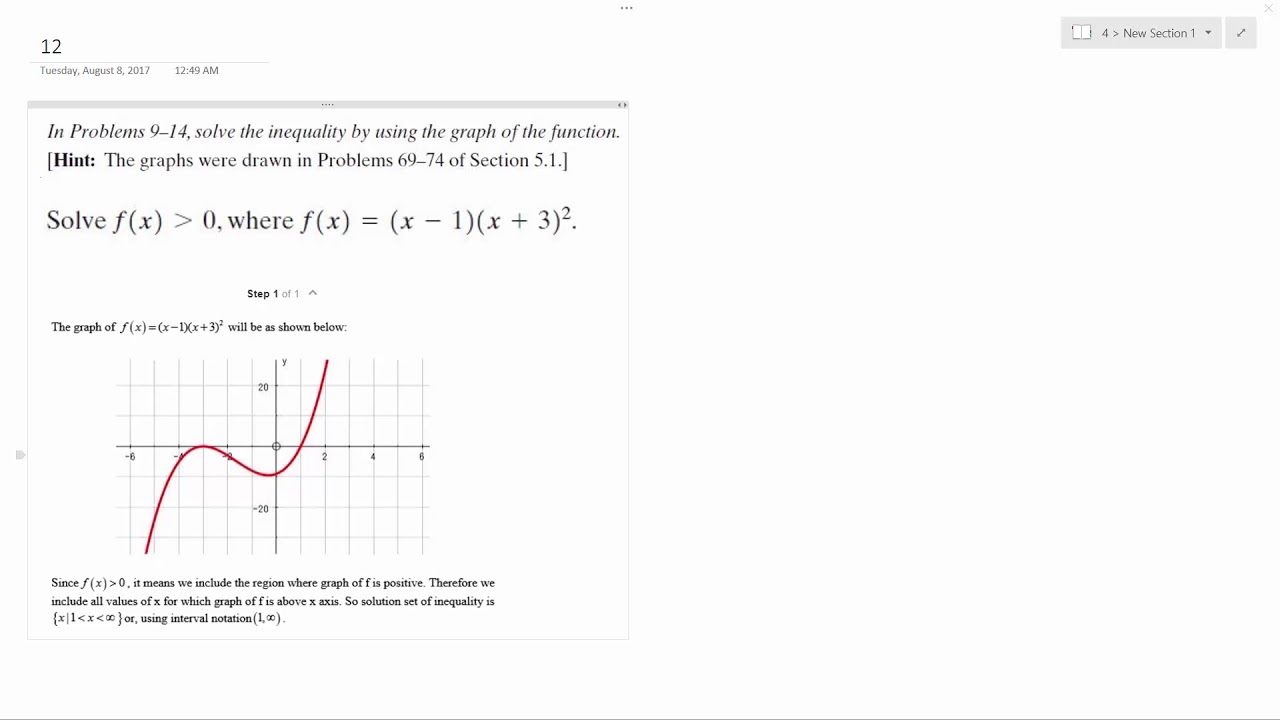



Solve F X Greater Than 0 Where F X X 1 X 3 2 Youtube



Activation Functions Fundamentals Of Deep Learning



Solution Use The Graph Of The Function To Estimate A F 2 B F 4 C All X Such That F X 0 I Can 39 T Show The Graph On Here It Won 39 T Copy And
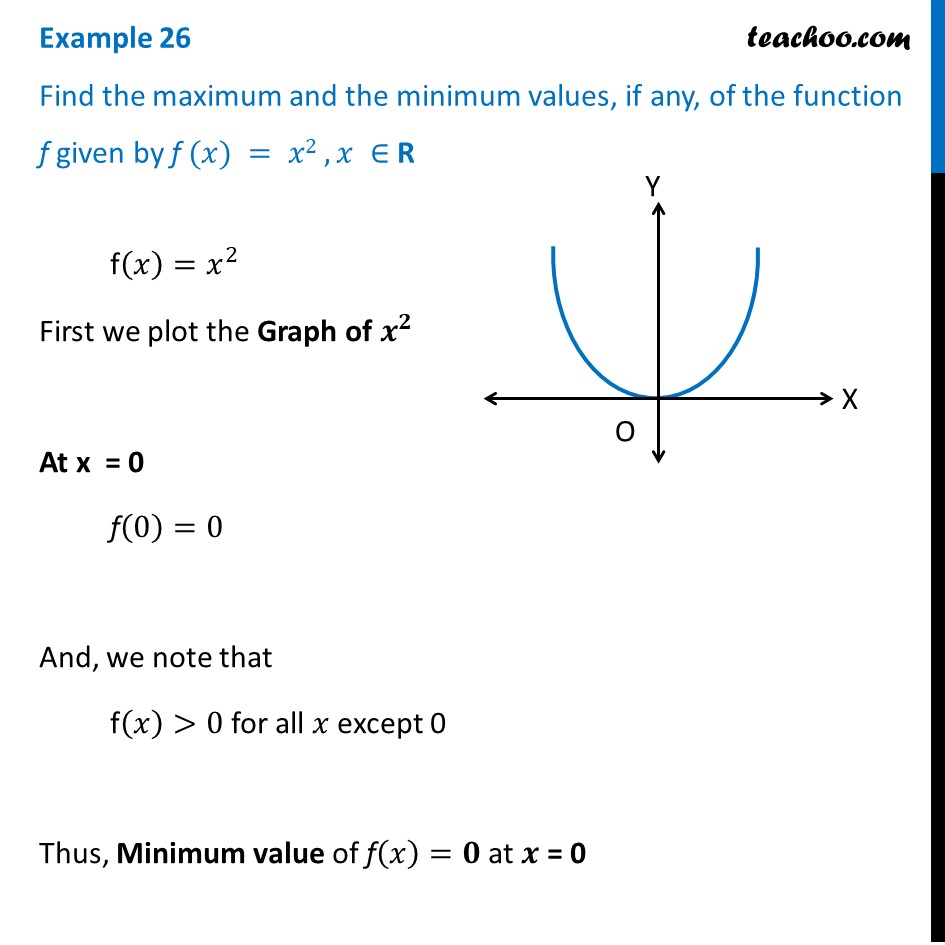



Example 26 Find Maximum And Minimum Values Of F X X2




Solving F X G X 0 Where F X E X 2 4 And The Graph Of G X Is Shown Mathematics Stack Exchange
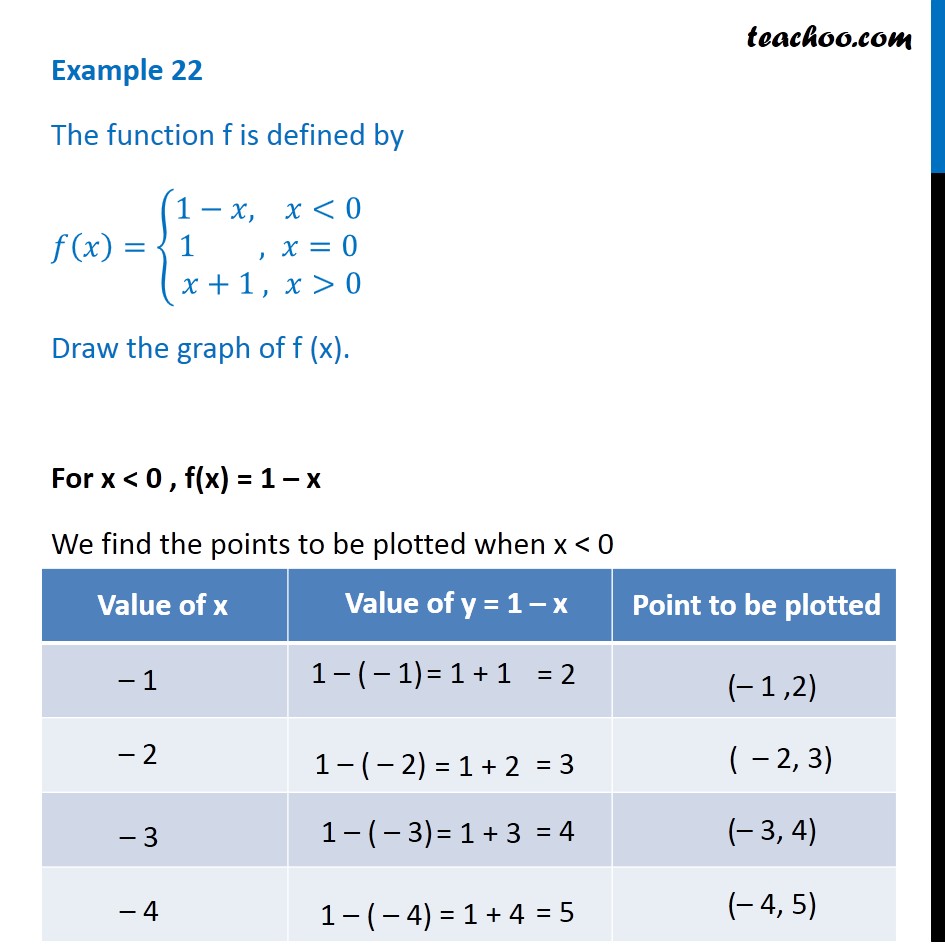



Example 22 Function F Is Defined By F X 1 X 1 X 1
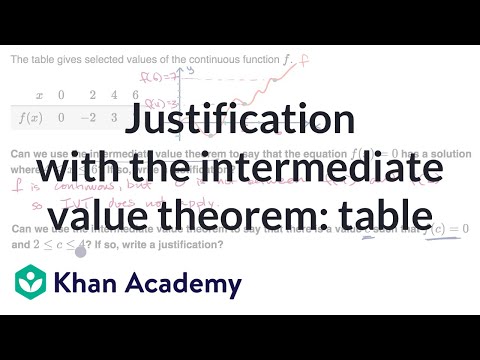



Justification With The Intermediate Value Theorem Table Video Khan Academy
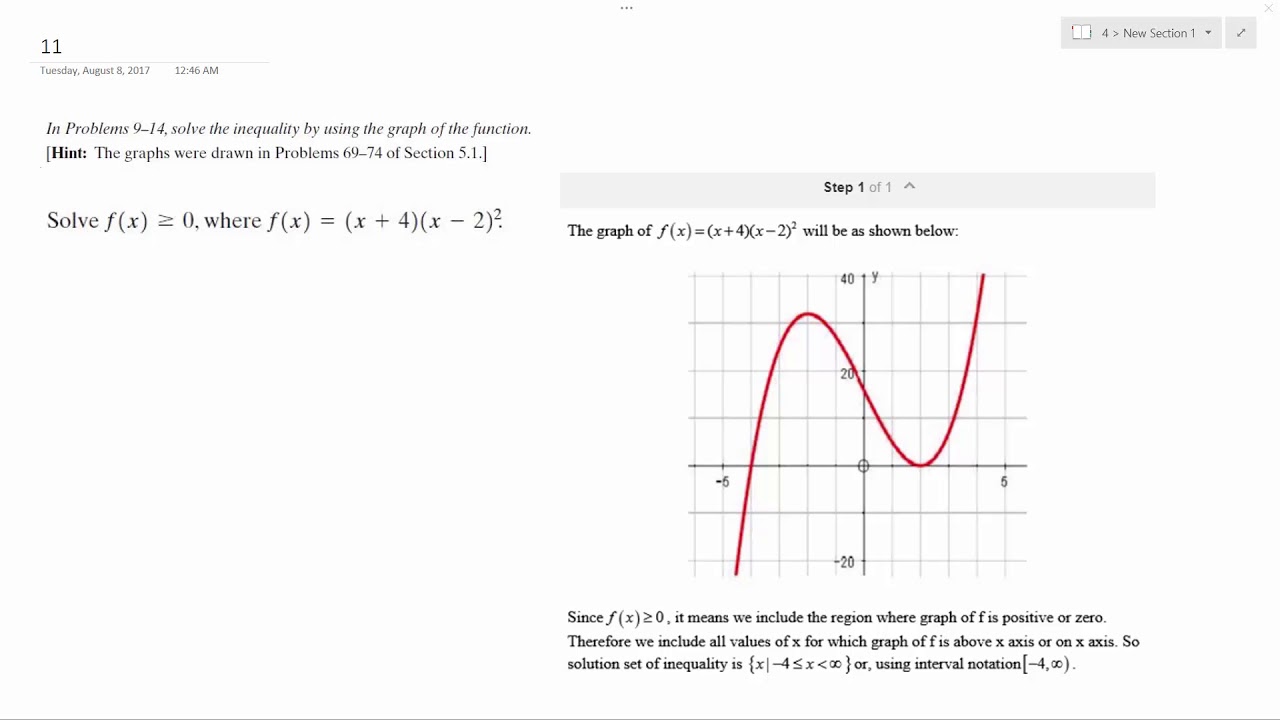



Solve F X Greater Than 0 Where F X X 4 X 2 2 Youtube
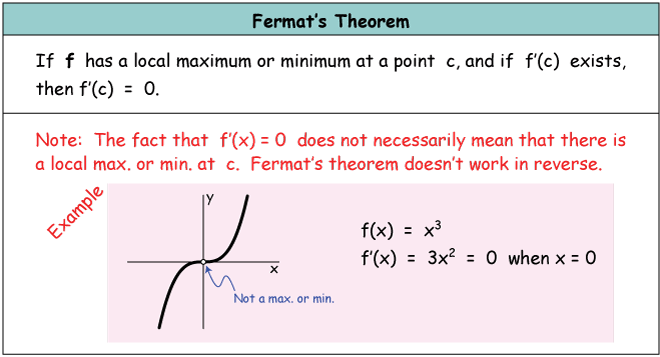



Reading Curve Sketching Business Calculus
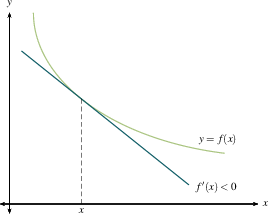



F Vs F




4 1 Extreme Values Of Functions Mathematics Libretexts



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Apc Ap07 Calculus Ab Form B Q6 Pdf




If F X 0 For All X Then A F X F X For Every Chegg Com




A Function F R R Satisfies The Equation F X Y F X F Y For All Xy E R F X 0 Suppose That The Function Is Differentiable At X 0 And F 0 2 Prove That F X Mathematics Topperlearning Com A5z3qnjj



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q5 Pdf




Given F Integrable And Int E F Geq 0 For Every E Measurable Set Prove F X Geq 0 Almost Everywhere Mathematics Stack Exchange
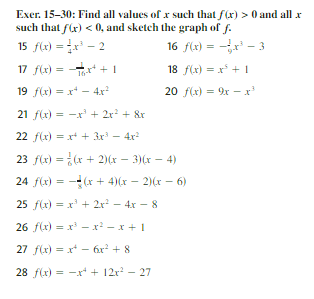



Find All Values Of X Such That F X 0 And All X Chegg Com



Math Usu Edu Rheal Math1210 Lecture Notes Review For Midterm 2 Concepts Pdf
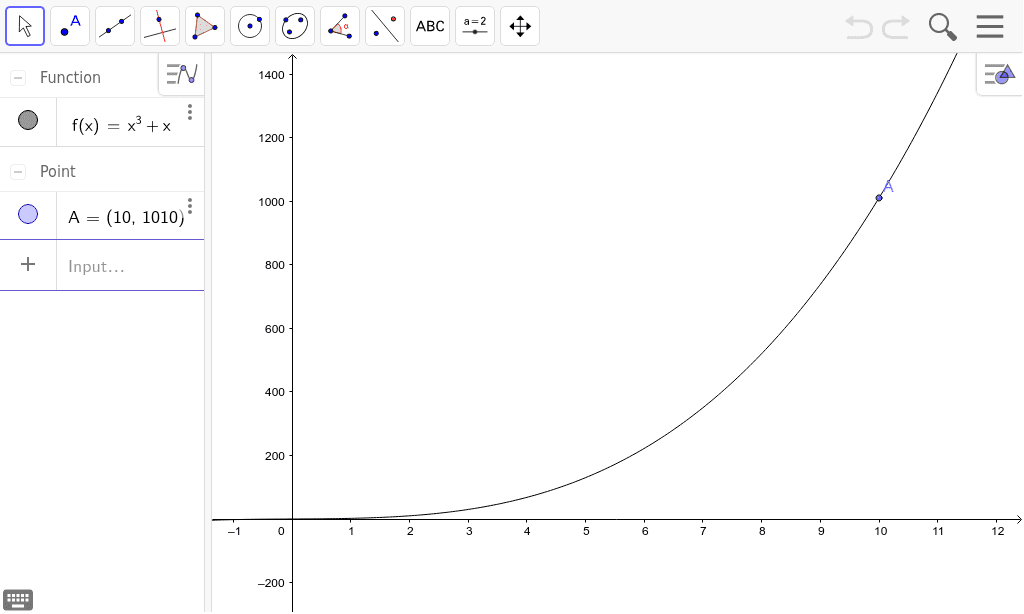



Graph Of F X X 3 X 0 X 10 Geogebra



What Is The Maclaurin Series X 0 For F X Sin 2x Socratic




Justification With The Intermediate Value Theorem Table Video Khan Academy




Derivative And Tangent Line



Discontinuous Functions




How Do I Prove If The Following Functions Are Differentiable At The Given Value Mathematics Stack Exchange




Let F X Is A Function Continuous For All X In Rexcept At X 0 Such That F X 0 X In Oo 0 And F X 0 X In 0 Oo If Lim X 0 F X 3
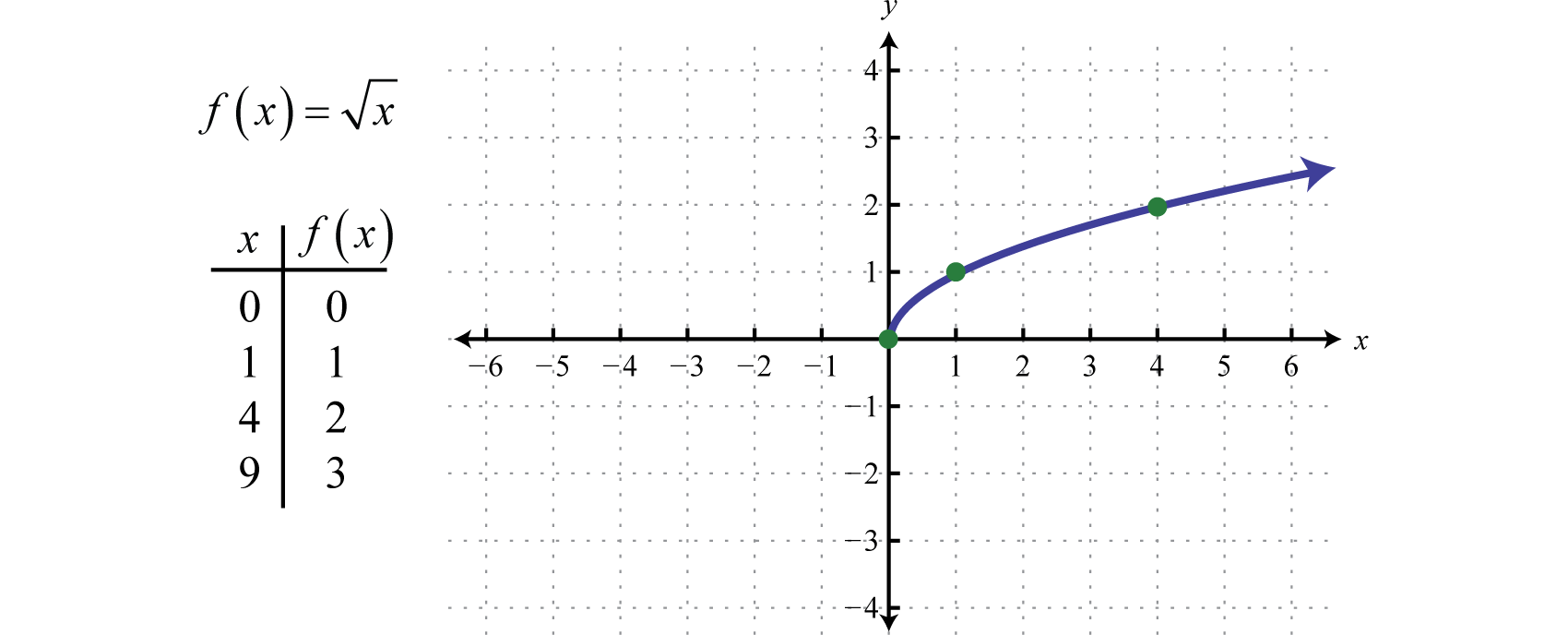



Graphing The Basic Functions



Calculus Questions With Answers 2



Increasing And Decreasing Functions



Inflection Points




4 3 How Derivatives Affect The Shape Of A Graph Mathematics Libretexts




Derivative And Tangent Line
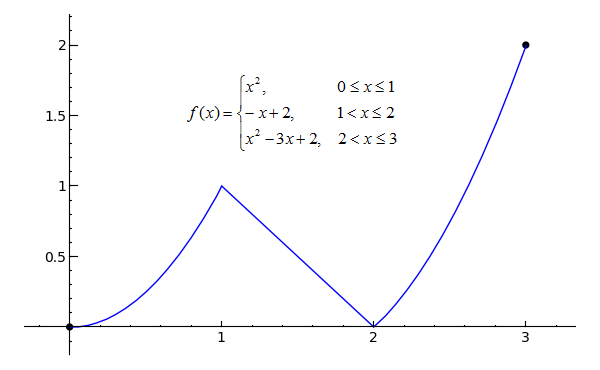



Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity




Let F X 0 And F X 0 For All X If X1 X2 Then



Comments
Post a Comment