[最も人気のある!] hazard ratio vs odds ratio 377264-Hazard ratio vs odds ratio
(Rate ratios are often interpreted as if they were risk ratios, eg, postmenopausal women using HRT had 047 times the risk of CAD compared to women not using HRT, but it is more precise to refer to the ratio of rates rather than risk) A cohort study is conducted to determine whether smoking is associated with an increased risk of bronchitis in adults over the age of 40 I just have a question regarding hazard ratios Are these similar to odds ratio?The adjusted odds ratios were derived using Cox proportional hazard regression In the unadjusted model, there is an increased risk of CVD in overweight participants as compared to normal weight and in obese as compared to normal weight participants (hazard ratios of 1215 and 1310, respectively) Hazard ratios (HRs) are used commonly to
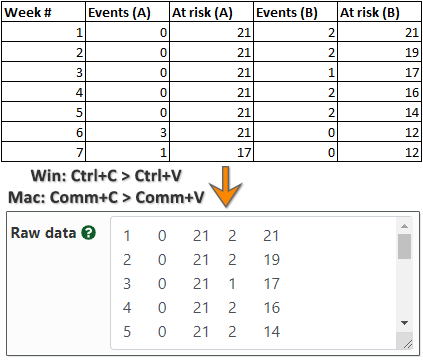
Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio
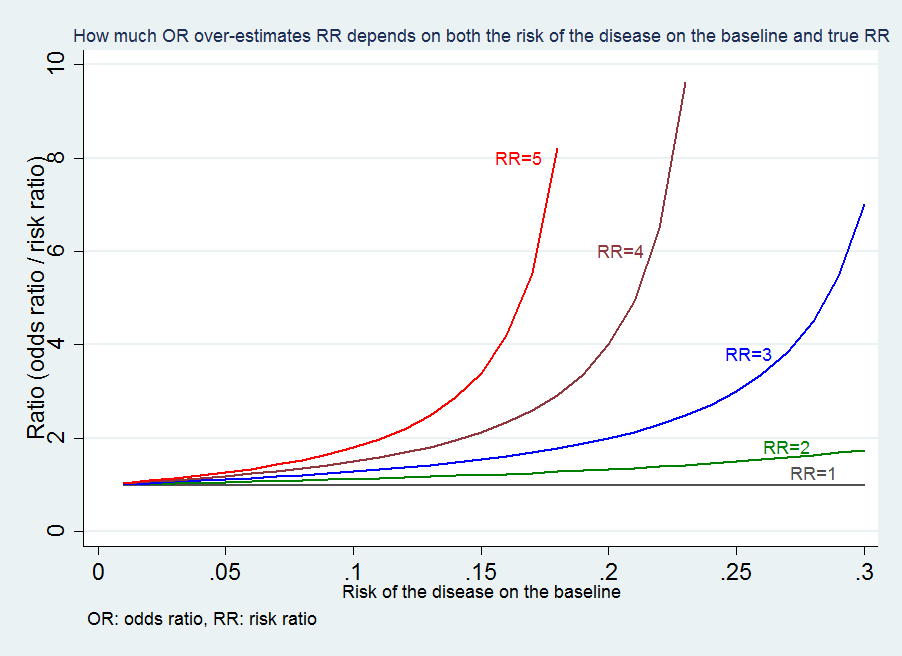
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio- The hazard ratio, sometimes called a relative hazard, is typically used to compare time to event data between two treatment groups The hazard ratio of death for the intervention group compared with the control group was 046 (022 to 095) The hazard ratio was derived as the ratio of the hazard of death for the intervention group to the hazard of death for theIn particular, it overstates the real effect the odds ratio is smaller than the relative risk for odds ratios 1 (eg it could lead to an overestimation of the real effect of a factor in increasing the




Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Efficacy And Safety Of Hydroxychloroquine And Chloroquine In The Treatment Of Covid 19
Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR One of the main differences between risk ratio and hazard ratio is that risk ratio does not care about the timingRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probability Again, the OR willData mentah tidak dilaporkan dengan cara menghitung odds ratio metaanalysis maka rasio hazard, odds, dan risiko relatif akan relatif dekat satu sama lain Jika bukan itu masalahnya, perbedaan mendasar antara tindakantindakan ini akan semakin terlihat Untuk durasi percobaan yang diberikan, distribusi tertentu untuk kejadian peristiwa dan pola dropout tertentu, ada
The hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold; The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group However, this wouldLogistic regression log (odds) = The hazard ratio of death for surgery vs no surgery is assumed to be the same at any time since baseline The model may therefore be called "a constant hazard ratio model", but someone thought that "proportional" is a better word to describe a fixed ratio of two hazards over time (When the ratio of two quantities is fixed, we may say that oneThe odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk (or odds) between the groups being compared An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora



Hazard And Odds Ratios Image Eurekalert Science News Releases
The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program At the start of the school year they impose the new tutoringAlgo nuevo pero que les servirá de mucho ;)RecuerdenConsecuencia a la Causa Estudio Casos y ControlesCausa a la Consecuencia Estudio Cohorte This too is sometimes brought into connection with the hazard ratio, although it is a measure of relative survival chances (control versus experimental treatment) rather than a measure of relative risk of death (experimental versus control treatment) The advantage of this perspective is that it follows naturally from a consideration of the survival distributions and does not require




Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Biostatistics Primer What A Clinician Ought To Know Hazard Ratios Sciencedirect
In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 1 In a randomised controlled trial, 441 patients assessed on admission as having low to moderate riskFor instance, a disease free survival was longer for an anastrozole group compared to a tamoxifen group;A logrank approach gives rise to a hazard ratio, and a variation of the Peto method for analysing timetoevent data gives rise to something in between The appropriate effect measure should be specified in RevMan Only fixedeffect metaanalysis methods are available in RevMan for 'O – E and




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Odds Ratio
Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 03 67 66 Hazard ratio (HR) Broadly equivalent to relative risk (RR); Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the raw numbers from the previous column (c) and therefore give different results than if the rounded numbers were used (eg, 006/008 = 075) The HR is usually calculated from a Cox proportional hazards model, which is one of the standardEssentially, the odds ratio estimate the _______ in these types of studies Risk ratio What is the definition of odds ratio?




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Younger Men With Prostate Cancer Have Lower Risk Of Upgrading While On Active Surveillance A Meta Analysis And Systematic Review Of The Literature Urology
The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a casecontrol study (see Lesson 1) A casecontrol study is based on enrolling a group of persons with disease ("casepatients") and a comparable group without disease ("controls") The number of persons in the control group is usually decided by the investigator Often, the size of the population from which the case Let's say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065 This is how you can interpret and report it The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of highcalorie diet The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a highcalorie diet mortality rate of smokers is 65% of that of gluttons AtAn odds ratio is the ratio of two odds In epidemiological parlance it is the odds of infection for those exposed to a risk factor, divided by the odds of infection for those not exposed to that




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Www Mdpi Com 72 6694 12 6 1673 Pdf
Peto's method applied to dichotomous data (Section 9442) gives rise to an odds ratio; Log odds and log hazard ratios have an unlimited ranges and can possibly apply to everyone This makes them good bases for studying heterogeneity of treatment effect When risk factors exist and a clinical trial enrolls patients having a variety of values of these risk factors, there will be outcome heterogeneity To easily account for known outcome heterogeneity, it is a goodFree thyroxine levels were positively associated with high coronary artery calcification score (odds ratio, 228;




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
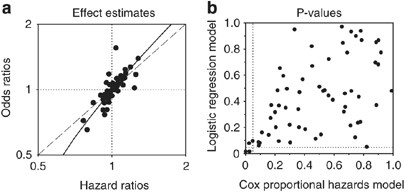



Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics
It is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratiosThe sample odds ratio n 11 n 00 / n 10 n 01 is easy to calculate, and for moderate and large samples performs well as an estimator of the population odds ratio When one or more of the cells in the contingency table can have a small value, the sample odds ratio can be biased and exhibit high variance Alternative estimators A number of alternative estimators of the odds ratio have beenOdds ratio the ratio of cross products This is not true for relative risk Switching the rows or columns inverts the odds ratio For example, the odds ratio for no cough given a history of bronchitis = (247/26)/(1002/44) = 0417 = 1/2397 This is the reciprocal of the OR for cough There are only two possible odds ratios, as switching both




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table
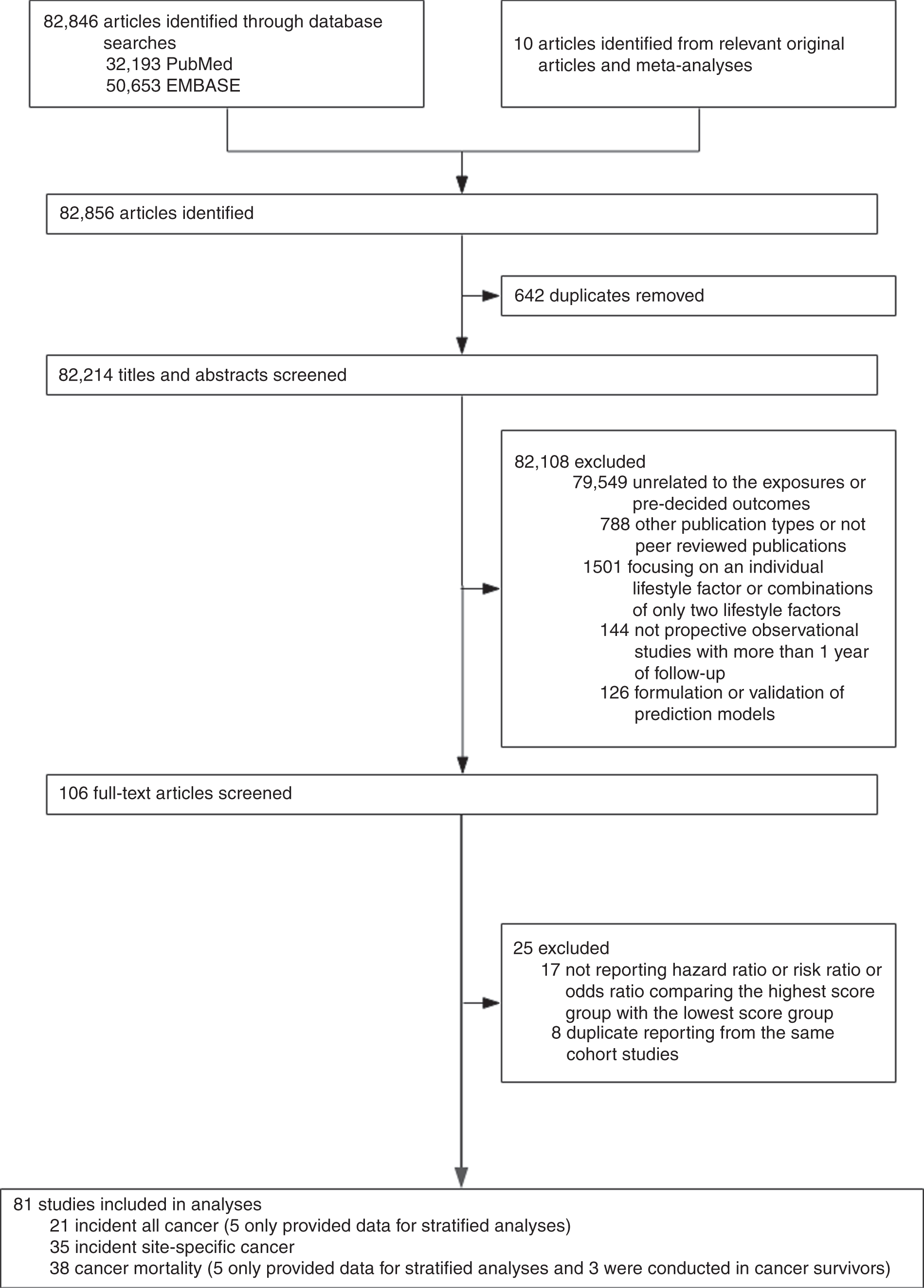



Combined Lifestyle Factors Incident Cancer And Cancer Mortality A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Prospective Cohort Studies British Journal Of Cancer
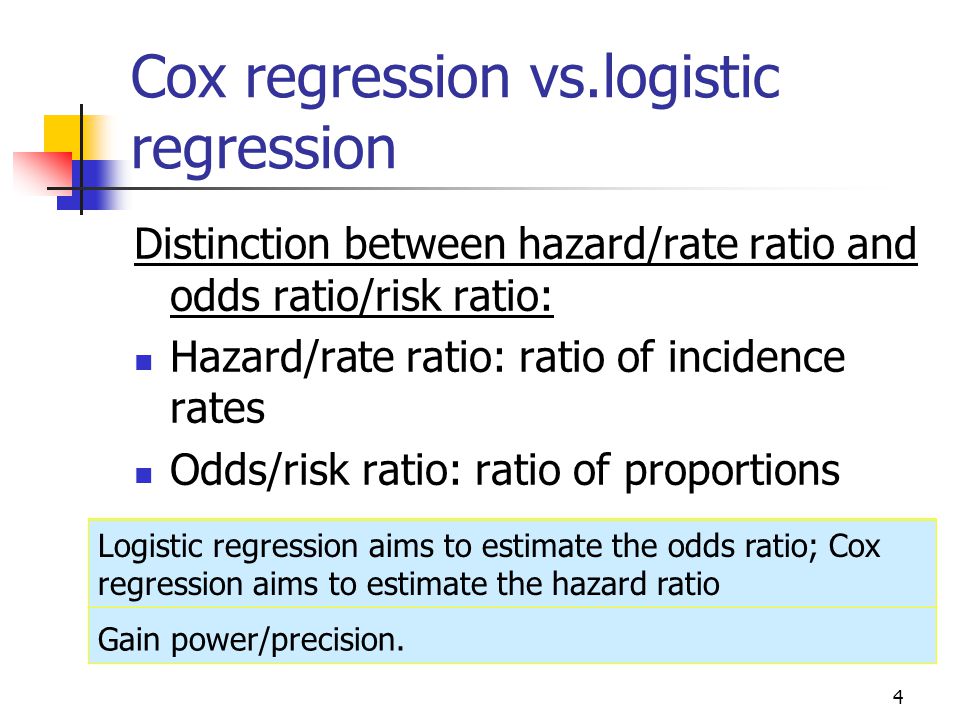
Cox regression aims to estimate the hazard ratio 10 Risks vs Rates Relationship between risk andThe method of presenting the results of clinical studies can affect their interpretation by clinicians2 and nonclinicians alike3,4 Therefore, it is important to understand the different ways in which results can be presented Absolute risk refers to the simple event rate in a group of people who receive an intervention (see Example 1) Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paper




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
Since all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type Risk reflects the proportion of persons experiencing the event, so it follows that comparing two cumulative incidences is called a risk ratio Relative Rate Rate is based on events per persontime = incidence rate Rate ratio = ratio of 2This implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 × 2 table with an odds ratios of 400Risk, absolute risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio These figures help to determine if the new treatment has an advantage over other treatments or placebo Ways of expressing treatment effects The absolute risk, number needed to treat, relative risk and odds ratio can be calculated by compiling a 2x2 table of study data Values can then be derived using the equations shown in the



Statistics For Medical Students Geeky Medics




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id
In simple terms we can therefore state that a hazard is the rate at which an event occurs (risk x time) and a hazard ratio is a the ratio of that rate from two differing groups In other words, the hazard ratio is a relative risk, when there is an interest in the timing of that risk For example, while a relative risk might not be able to show that a treatment has an effect because both groups The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;Useful when the risk is not constant with respect to time It uses information collected at different times The term is typically used in the context of survival
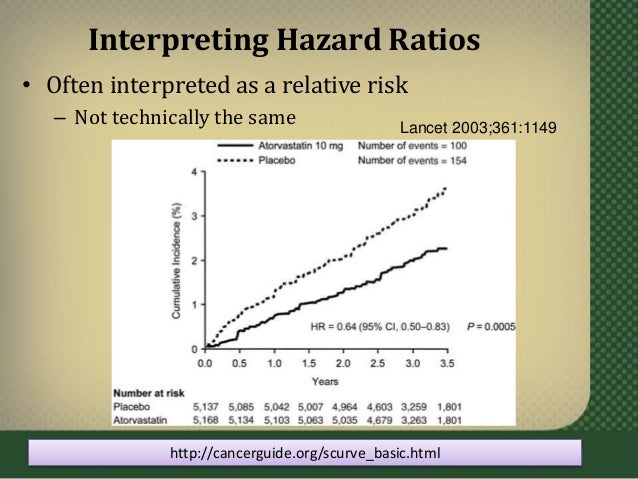



Hazard Ratios



Coefplot Plotting Regression Coefficients And Other Estimates In Stata
And the statistic given was "hazard ratio 0 (95% CI , p value=0013) from this statistic I understand it is statistically significant, with a p value below 005 But would you beThey wrote "The hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint first" In a trial of treatment to shorten the duration of symptoms in herpes zoster, for example, the hazard ratio represents the odds that the time to remission of symptoms is less in a patient from the treatment than from the control group The Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized Keywords hazard ratio



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像
Ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Logistic regression aims to estimate the odds ratio;Relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a study if there are no events in the control group This is




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Thread By Profdfrancis Risk Ratio Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio 2nd And Final Part Of The Tweetorial From Orbita Hq Fun Easy And Informativ Meded Foamed Cardiology Cardiotwitter
Comparative Trials Odds ratio, hazard ratio Types of Variables The point estimate you choose depends on the "nature" of the outcome of interest Continuous Variables Examples change in tumor volume or tumor diameter Commonly used point estimates mean, median Binary Variables Examples response, progression, > 50% reduction in tumor size Commonly used point estimateRealRisk works with any study which investigates the link between a risk factor or intervention and an outcome of interest, which also reports one of the following a relative risk (RR), hazard ratio (HR), odds ratio (OR) or a percentage change The study can be observational or experimental in design The terminology used can vary – so don't be put off if the terms 'risk factor' andObserved odds ratio = Approximate power (for 5% significance) = 9684% Approximate (Woolf, logit) 95% confidence interval = to Conditional maximum likelihood estimates Conditional estimate of odds ratio = Exact Fisher 95% confidence interval = to Exact Fisher one sided P < , two sided P < Exact midP




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Study Mortality With Hazard Rates Not Probabilities Biorxiv
An odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratio suggests a strong association Once the odds ratio is determined, tests of statistical significance must be used to determine theRelative risk vs Odds ratio Similaritie Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio, HR The relative risk is the ratio of the risk in the exposed group to the risk in the unexposed group, as is summarized in Box 1 Depending on the study design and statistical method applied, the relative risk can be presented using different measures of effect, such as the incidence rate ratio andThis is called the odds ratio;




Cetuximab And Chemotherapy As Initial Treatment For Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Nejm




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
An odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictor95% confidence interval, ) and incident ASCV events (hazard ratio, 187This video wil help students and clinicians understand how to interpret hazard ratios



Plos One Pcsk9 Loss Of Function Variants And Risk Of Infection And Sepsis In The Reasons For Geographic And Racial Differences In Stroke Regards Cohort
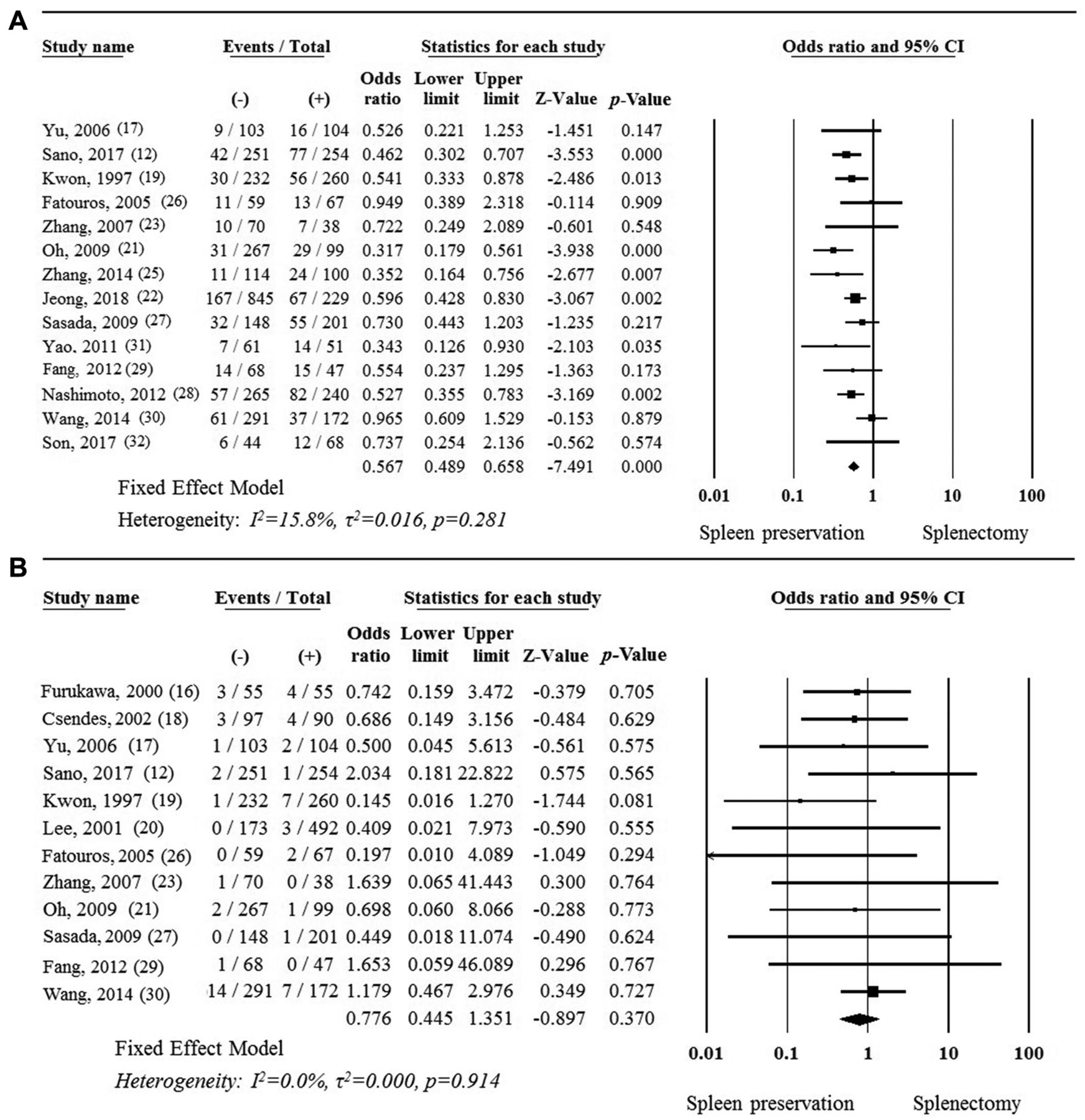



Systemic Review And Meta Analysis Of Impact Of Splenectomy For Advanced Gastric Cancer In Vivo
Odds ratio (OR) Hồi qui logistic (logistic regression) Cắt ngang (crosssectional) Prevalence ratio (PR) hay OR Hồi qui nhị phân (binomial regression) hay Hồi qui logistic Theo thời gian (prospective) Relative risk (RR) Hồi qui Cox (Cox's regression model) Thử nghiệm lâm sàng RCT RR hay Hazard ratio (HR)Odds that a person with an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed)/ Odds that a person without an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed) Odds group 1/odds group 2
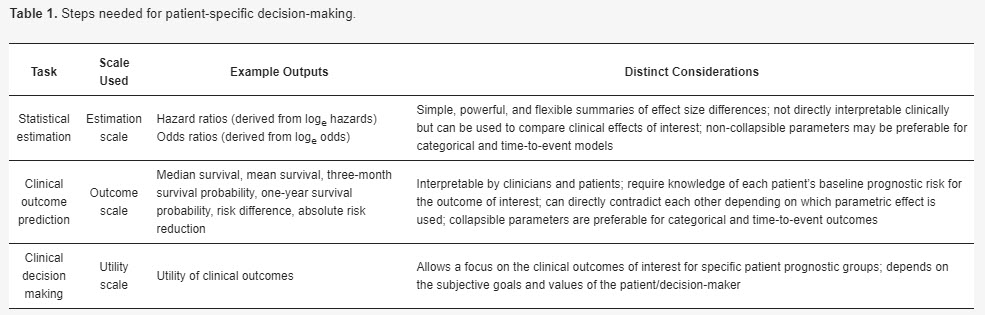



Should One Derive Risk Difference From The Odds Ratio Bayes Datamethods Discussion Forum



Statistics 262 Intermediate Biostatistics Ppt Video Online Download




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Various Estimates For The Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Of Herpes Download Table




Study Mortality With Hazard Rates Not Probabilities Biorxiv




Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Efficacy And Safety Of Hydroxychloroquine And Chloroquine In The Treatment Of Covid 19
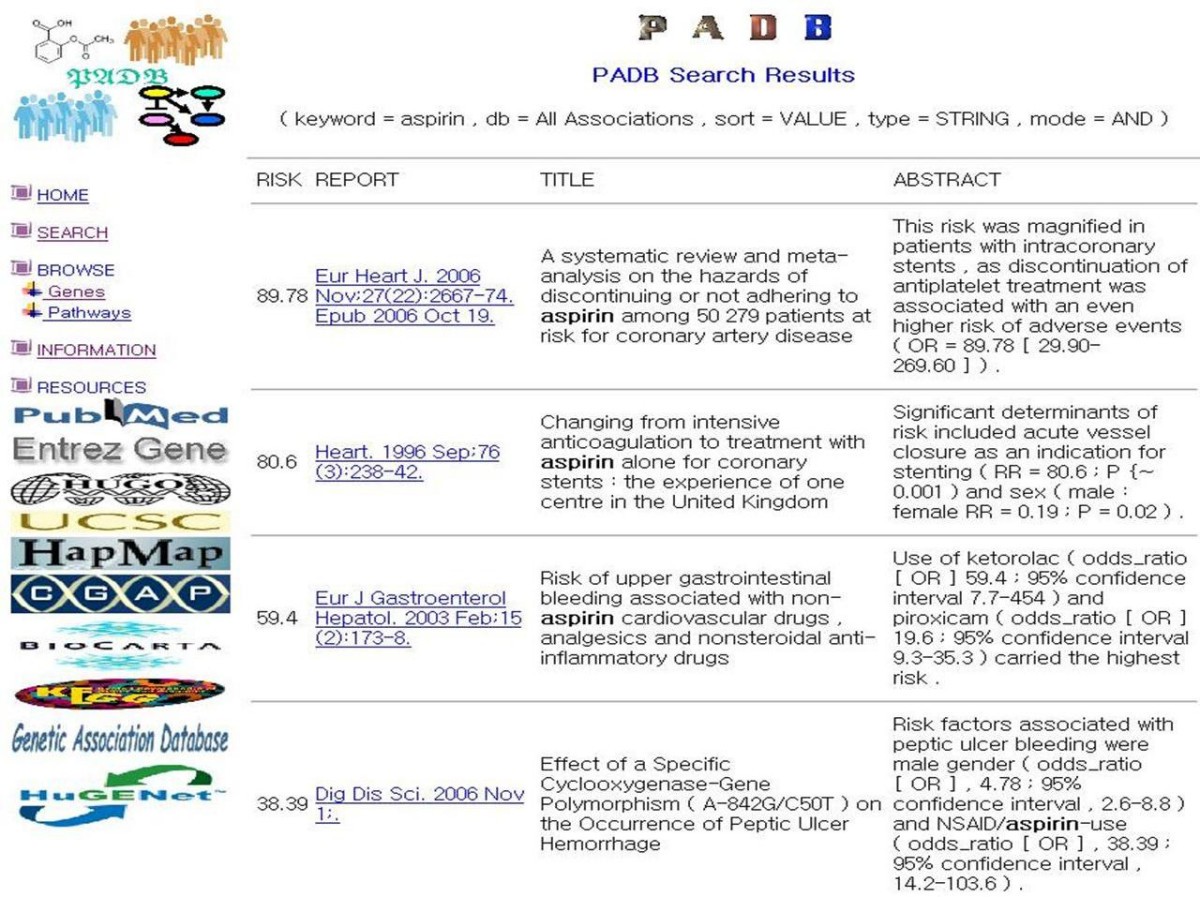



Padb Published Association Database Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Introduction To Biostatistics For Clinical And Translational Researchers



1




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Stat D Si Relative Risk Pdf4pro



Plos One Delirium As A Predictor Of Mortality And Disability Among Hospitalized Patients In Zambia
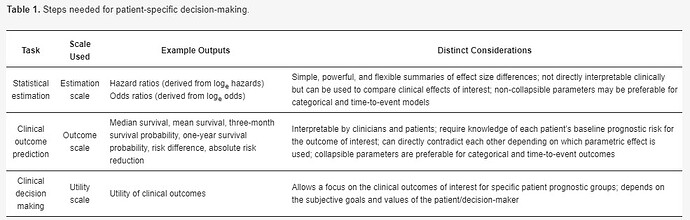



Should One Derive Risk Difference From The Odds Ratio Bayes Datamethods Discussion Forum




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Hazard Ratio




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Survival Analysis In Assessment Of Influence Of The Sars Cov 2 Pandemic On Probability And Intensity Of Decline In The Value Of Stock Indices Research Square




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
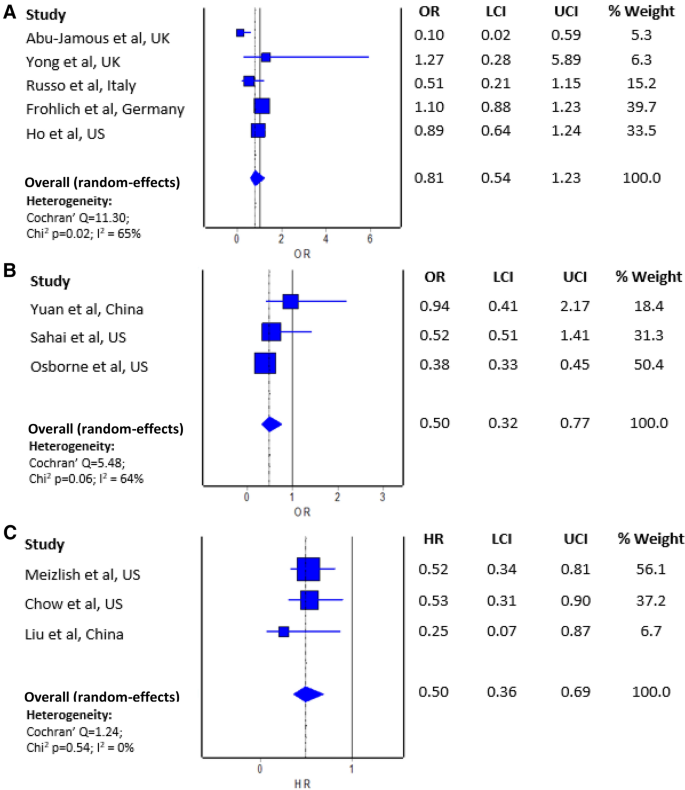



Use Of Antiplatelet Drugs And The Risk Of Mortality In Patients With Covid 19 A Meta Analysis Springerlink




Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller
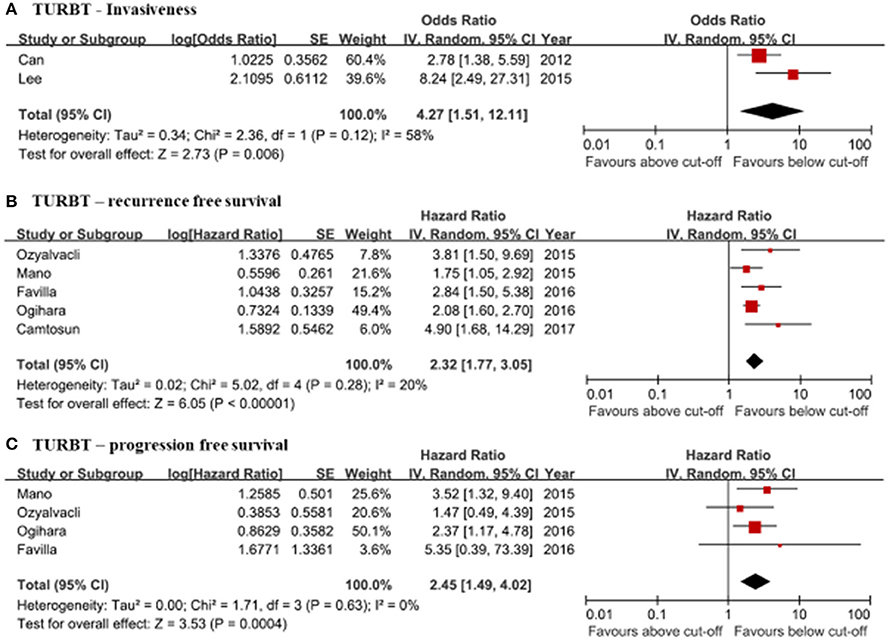



Frontiers Clinical Significance Of Pre Treated Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio In The Management Of Urothelial Carcinoma A Systemic Review And Meta Analysis Oncology




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia
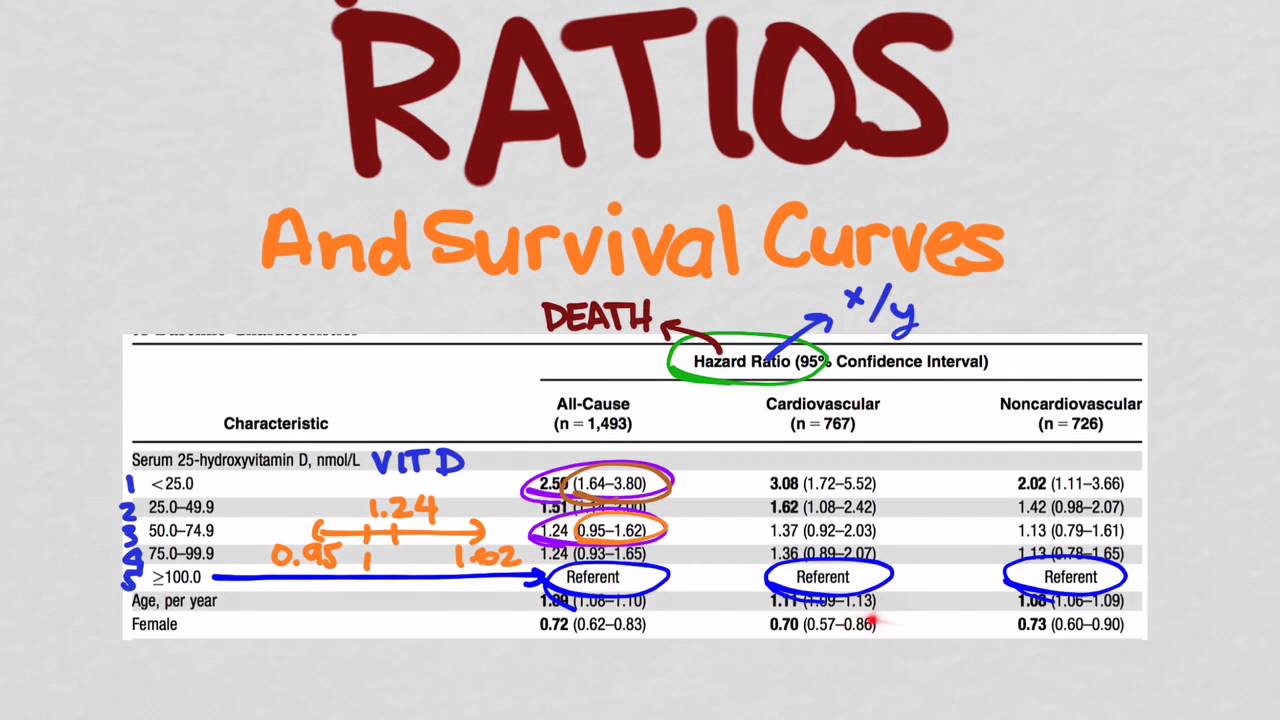



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube




Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Hazard Ratios For Progression Free And Overall Survival And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram




Ctspedia Ctspedia Clinaegraph001



Http Imaging Mrc Cbu Cam Ac Uk Statswiki Faq Meta Action Attachfile Do Get Target Cochraneor Pdf




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




Association Of Bmi Diabetes And Risk Of Tuberculosis A Population Based Prospective Cohort International Journal Of Infectious Diseases




Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Www Jstor Org Stable



Bmjopen Bmj Com Content Bmjopen 6 12 E Dc1 Embed Inline Supplementary Material 1 Pdf Download True




Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv
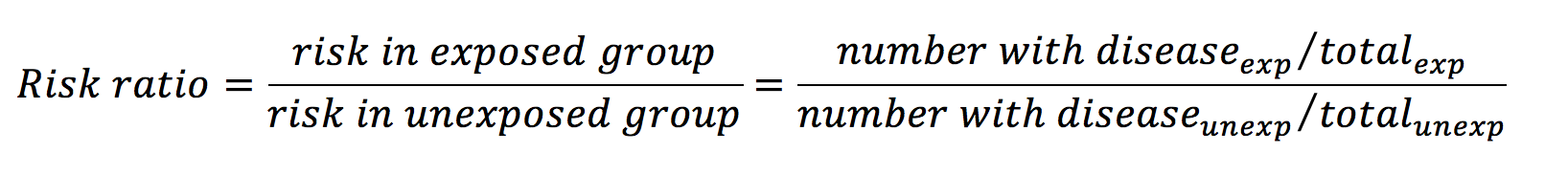



Statistics For Medical Students Geeky Medics




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
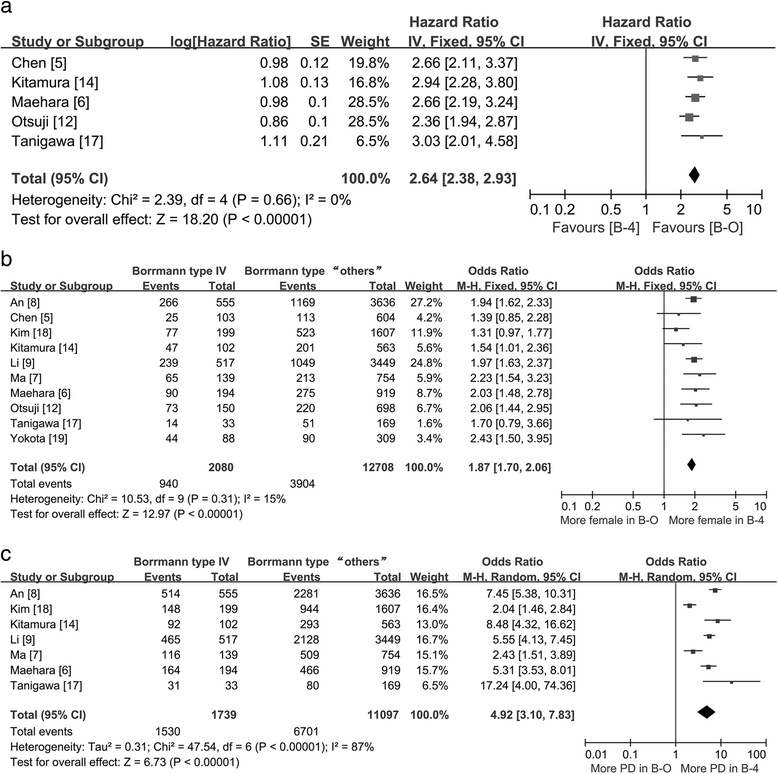



Clinicopathologic Characteristics And Prognosis Of Borrmann Type Iv Gastric Cancer A Meta Analysis World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text



Potential Misinterpretation Of Treatment Effects Due To Use Of Odds Ratios And Logistic Regression In Randomized Controlled Trials




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id
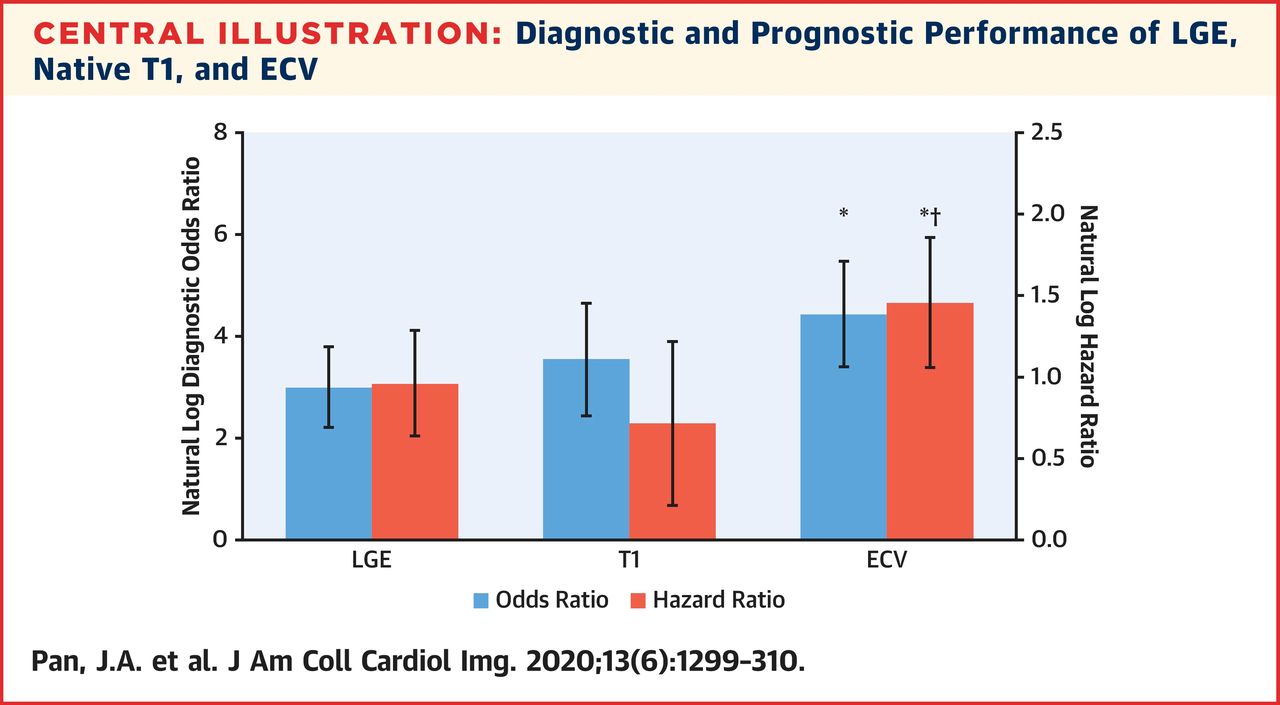



Jacc Journals Jaccimg Explores Cmr In Cardiac Amyloidosis T1 Mapping Has Similar Sensitivity Specificity While Avoiding Contrast Ecv Has Highest Diagnostic Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio For Adverse Events




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Help With Differentiating Relative Risk Odds Ratio Ar Usmle Forums




Comparison Of Tenofovir Versus Entecavir On Reducing Incidence Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Gu Journal Of Gastroenterology And Hepatology Wiley Online Library




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Design And Analysis Of Clinical Study Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Dr Tuan V Nguyen Garvan Institute Of Medical Research Sydney Australia Ppt Download




Pooled Hazard Ratio For Overall Survival A Progression Free Survival Download Scientific Diagram
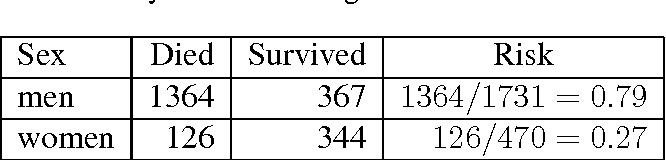



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table




Lincom Stata




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



1
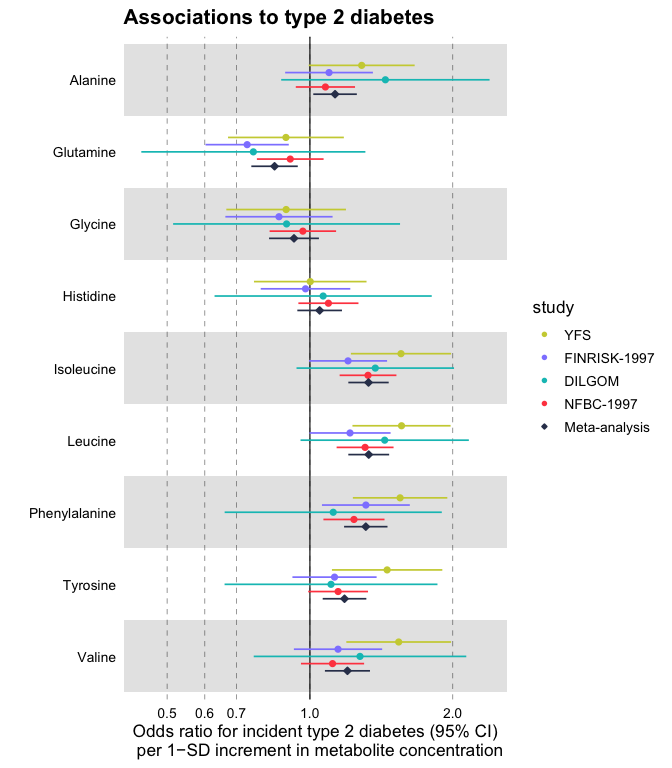



Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot



Plos One Influence Of Clinicopathological Characteristics And Comprehensive Treatment Models On The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




Abc Transporter Genes And Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes Care



Comments
Post a Comment